Sterilization is a critical component of dental care, playing a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of patients.
In a dental setting, where the risk of cross-contamination is high, maintaining strict sterilization protocols is essential. This blog post delves into the concept of dental sterilization, its processes, and its importance.
We will explore the setup of sterilization areas in dental offices, common methods of heat sterilization, and the market outlook for dental sterilization products.
Additionally, we will discuss best practices for maintaining sterilization standards and the role of technology in advancing sterilization methods.
What is Sterilization in Dentistry?
Sterilization in dentistry refers to the process of eliminating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from dental instruments and surfaces.
This process ensures that all equipment used in dental procedures is free from potentially harmful microorganisms that could lead to infections. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, which only reduces the number of microorganisms to a safe level.
In dentistry, complete sterilization is essential to prevent cross-contamination and protect both patients and healthcare providers.

Dental Sterilization Process
The dental sterilization process involves several steps to ensure that instruments and surfaces are completely free from contaminants. These steps include:
Pre-Cleaning: Instruments are rinsed or wiped to remove visible debris and biological material. This step helps reduce the microbial load and makes subsequent sterilization more effective.
Cleaning: Instruments are thoroughly cleaned using ultrasonic cleaners, enzymatic solutions, or manual scrubbing. This step removes remaining organic and inorganic materials.
Rinsing and Drying: Instruments are rinsed with water and then dried to prevent water spots or rusting.
Packaging: Clean and dry instruments are packaged in sterilization pouches or wraps. The packaging is essential for maintaining sterility until the instruments are used.
Sterilization: The packaged instruments are placed in a sterilizer, where they undergo heat sterilization or another method to eliminate all microbial life.
Storage: Sterilized instruments are stored in a clean, dry area until they are needed. Proper storage helps maintain the sterility of the instruments.
Importance of Sterilization in Dentistry
Sterilization is crucial in dentistry for several reasons:
Patient Safety: Proper sterilization prevents the transmission of infectious diseases, ensuring that patients are not exposed to harmful pathogens during dental procedures.
Compliance with Regulations: Dental practices are required by law to follow strict sterilization protocols. Compliance with these regulations helps avoid legal issues and ensures that the practice meets health and safety standards.
Professional Reputation: A commitment to high standards of sterilization enhances the reputation of a dental practice. Patients are more likely to trust and return to a practice that prioritizes their safety.
Protection of Staff: Sterilization not only protects patients but also safeguards dental staff from exposure to infectious agents.

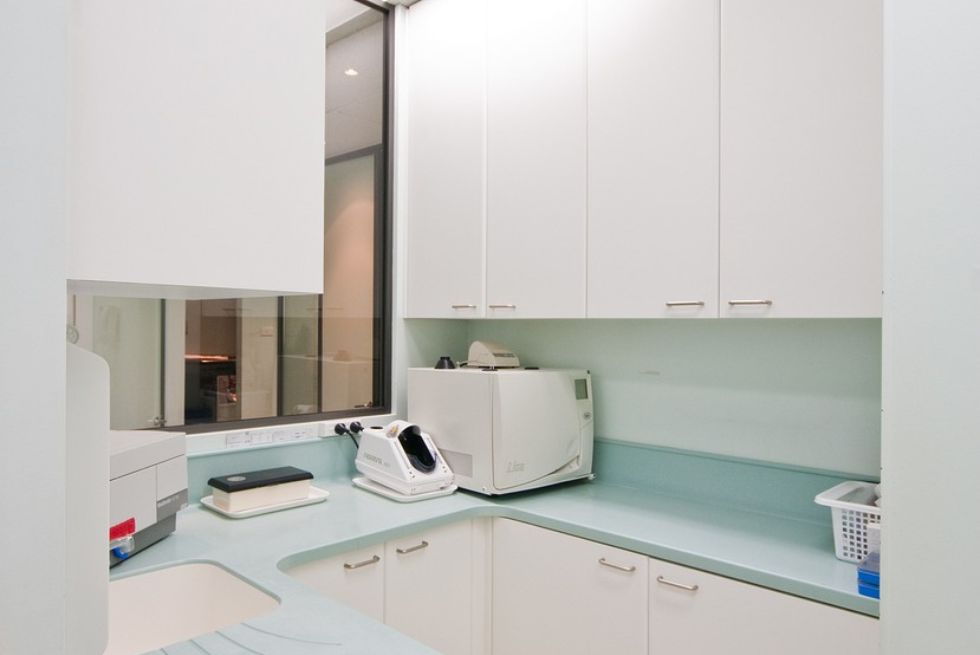
Dental Office Sterilization Area
The sterilization area in a dental office is a designated space where instruments are cleaned, disinfected, and sterilized. This area is typically divided into distinct zones to prevent cross-contamination:
Receiving and Cleaning Area: In this zone, contaminated instruments are received, cleaned, and prepped for sterilization. It includes sinks, ultrasonic cleaners, and other cleaning equipment.
Preparation and Packaging Area: Cleaned instruments are inspected, dried, and packaged in this zone. It often includes drying equipment and sealing machines for sterilization pouches.
Sterilization Area: This zone houses sterilizers such as autoclaves and dry heat ovens. Instruments are sterilized here before being moved to the storage area.
Storage Area: Sterilized instruments are stored in a clean environment until they are needed for patient care.
Maintaining a well-organized and clearly defined sterilization area is essential for ensuring that instruments are processed correctly and remain sterile until use.
Which is a Common Method of Heat Sterilization in a Dental Office?
A common method of heat sterilization used in dental offices is the autoclave, which uses steam under pressure to sterilize instruments.
Autoclaves are highly effective because the combination of heat and pressure kills all forms of microbial life, including spores.
The typical cycle involves heating the instruments to a temperature of 121-134°C (250-273°F) for a specified time, depending on the type of load and materials being sterilized.
Another method is dry heat sterilization, which involves heating instruments in an oven at temperatures of 160-180°C (320-356°F). This method is suitable for items that may be damaged by moisture or steam, such as certain dental handpieces and instruments.
Both methods are widely used in dental practices due to their effectiveness, efficiency, and ability to sterilize a wide range of instruments and materials.

Dental Sterilization Market Outlook
The market for dental sterilization products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of infection control, stringent regulations, and the rising number of dental procedures. Key trends in the market include:
Technological Advancements: Innovations in sterilization technology, such as more efficient autoclaves and sterilization indicators, are improving the effectiveness and efficiency of sterilization processes.
Growing Demand for Disposable Products: There is a growing preference for disposable instruments and materials, which reduce the need for sterilization and the risk of cross-contamination.
Regulatory Compliance: Stricter regulations and guidelines for infection control are driving the demand for high-quality sterilization products and equipment.
Increased Focus on Patient Safety: Dental practices are increasingly prioritizing patient safety, leading to greater investment in sterilization infrastructure and training.
Best Practices for Maintaining Sterilization Standards
To maintain high sterilization standards in dental practices, the following best practices should be observed:
Regular Training: Staff should receive ongoing training on sterilization protocols and the proper use of equipment.
Routine Maintenance: Sterilization equipment should be regularly maintained and serviced to ensure it operates correctly and effectively.
Use of Indicators: Biological, chemical, and mechanical indicators should be used to monitor and verify the effectiveness of the sterilization process.
Proper Documentation: Keeping detailed records of sterilization cycles, equipment maintenance, and staff training helps ensure compliance with regulations and provides a record of the practice's commitment to patient safety.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Sterilization Methods
Technology plays a pivotal role in advancing sterilization methods in dentistry. Innovations such as:
Automated Sterilization Systems: These systems offer precise control over sterilization parameters, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring consistent results.
Digital Tracking and Documentation: Modern sterilization systems often include digital tracking and documentation features, making it easier to maintain records and ensure compliance.
Improved Sterilization Indicators: Advances in sterilization indicators provide more accurate and reliable verification of sterilization effectiveness, enhancing patient safety.
These technological advancements not only improve the efficiency and effectiveness of sterilization processes but also contribute to better overall patient care.
Conclusion
Sterilization is a cornerstone of dental practice, crucial for ensuring patient safety and maintaining high standards of care. By understanding the processes, importance, and best practices associated with dental sterilization, dental professionals can provide safe and effective treatment to their patients.
As the dental sterilization market continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and regulatory requirements, dental practices must stay informed and equipped to meet these challenges.
Ultimately, a commitment to rigorous sterilization protocols is essential for the success and reputation of any dental practice, ensuring a safe environment for both patients and staff.