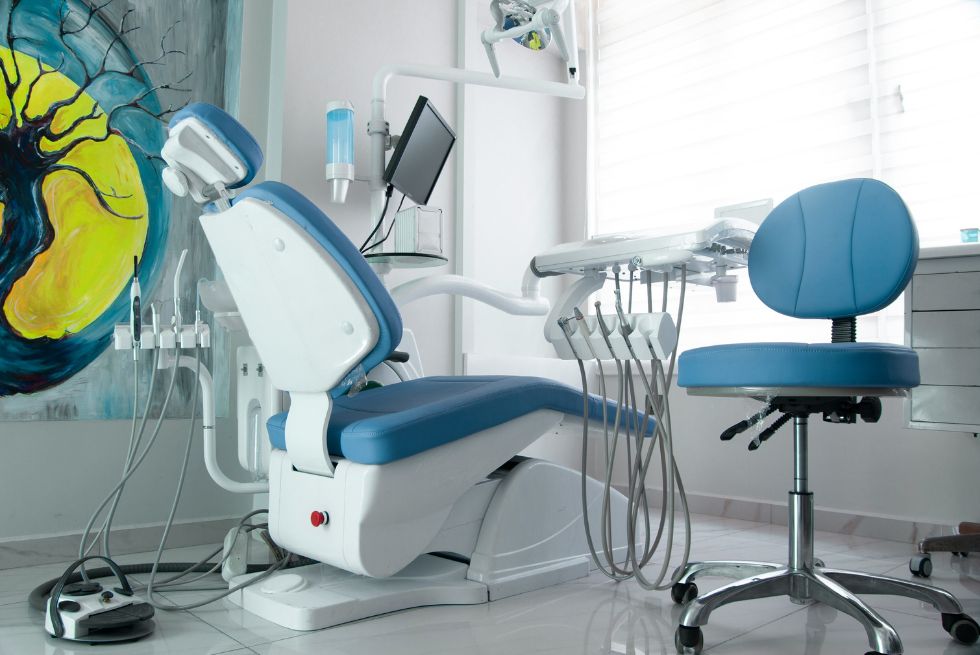
Dental chair positions play a critical role in delivering effective and efficient dental care. The right chair position ensures that both the dentist and the patient are comfortable, allowing for optimal access and visibility during procedures.
Understanding various dental chair positions for patient can enhance the quality of dental treatments, improve patient comfort, and reduce the risk of injury for dental professionals.
This article will explore the different dental chair positions, including upright, subsupine, semi-supine, supine, Trendelenburg, pregnant, and Fowler's positions, detailing their uses and benefits.
Upright Position in Dental Chair
Description
The upright position in a dental chair refers to the chair backrest being positioned at a 90-degree angle to the seat, allowing the patient to sit upright.
Uses
Initial Consultations: Ideal for patient interviews and discussions before any dental procedure.
Impressions and X-rays: Useful for taking dental impressions and certain types of X-rays.
Patient Education: Facilitates clear communication between the dentist and the patient, allowing for easy explanation of treatment plans and procedures.
Benefits
Communication: Promotes face-to-face interaction, enhancing patient understanding and comfort.
Accessibility: Allows patients to easily get in and out of the chair, which is especially important for elderly or disabled patients.
Comfort: Provides a familiar and less intimidating position for patients during non-invasive examinations.

Subsupine Position in Dental Chair
Description
The subsupine position involves tilting the dental chair so that the patient's head is lower than their heart and feet. This position is slightly beyond the horizontal plane.
Uses
Oral Surgery: Often used during surgical procedures to control bleeding and improve access.
Medical Emergencies: Useful in managing patients who may faint (syncope) by promoting blood flow to the brain.
Complex Procedures: Enhances visibility and access for detailed dental work.
Benefits
Blood Flow: Promotes better circulation, which is critical during lengthy procedures.
Visibility: Provides the dentist with an enhanced view of the oral cavity, facilitating precision work.
Safety: Helps manage potential medical emergencies effectively within the dental office setting.
Semi-Supine Position in Dental Chair
Description
In the semi-supine position, the dental chair is reclined at an angle between the upright and supine positions, typically around 45 degrees.
Uses
General Dentistry: Suitable for various routine procedures like cleanings, fillings, and minor restorations.
Patient Comfort: Ideal for patients who may have difficulty lying completely flat due to medical conditions.
Benefits
Comfort: Provides a balance between accessibility for the dentist and comfort for the patient.
Versatility: Can be used for a wide range of dental procedures, making it a practical choice in many situations.
Reduced Anxiety: Less intimidating than the fully reclined supine position, helping to ease patient anxiety.
Supine Position in Dental Chair
Description
The supine dental chair position has the patient lying flat on their back, with the chair fully reclined to a horizontal position.
Uses
Comprehensive Procedures: Commonly used for most dental treatments including examinations, fillings, root canals, and extractions.
Optimal Access: Provides the best access and visibility for the dentist to perform precise work.
Benefits
Ergonomics: Allows the dentist to work in a comfortable, natural posture, reducing the risk of strain and injury.
Patient Comfort: Evenly distributes the patient's weight, reducing pressure points and discomfort.
Accessibility: Ensures that the dentist has an unobstructed view of the oral cavity for detailed procedures.

Trendelenburg Position in Dental Chair
Description
In the trendelenburg position in dentistry, the patient's body is laid flat on their back with the feet elevated higher than the head.
Uses
Emergency Situations: Used to manage patients experiencing shock or a significant drop in blood pressure.
Surgical Access: Occasionally used to improve surgical access and control bleeding during certain procedures.
Benefits
Improved Circulation: Enhances venous return to the heart, which can be crucial in emergency scenarios.
Effective Management: Assists in managing hypotension and other medical emergencies within the dental office.
Pregnant Position in Dental Chair
Description
The pregnant position in a dental chair involves modifications to accommodate the unique needs of pregnant patients, ensuring their comfort and safety.
Uses
Routine Check-ups: Regular dental visits during pregnancy, addressing routine oral health issues.
Special Procedures: Adjustments may be needed for procedures requiring longer durations to ensure patient comfort.
Benefits
Comfort: Ensures the pregnant patient is comfortable and not in a position that could restrict blood flow.
Safety: Reduces the risk of supine hypotensive syndrome by avoiding lying flat on the back.
Accessibility: Allows the dentist to perform necessary procedures without compromising the patient’s well-being.
Fowler's Position in Dental Chair
Description
The Fowler's position involves positioning the dental chair with the backrest reclined at an angle between 45 to 60 degrees, often with the knees slightly elevated.
Uses
Post-Operative Recovery: Used for patients recovering from surgical procedures.
Respiratory Issues: Beneficial for patients with respiratory conditions, providing easier breathing.
Benefits
Breathing Ease: Facilitates easier breathing for patients with respiratory problems or those recovering from anesthesia.
Comfort: Provides a comfortable resting position post-procedure.
Patient Care: Enhances overall patient care and comfort during recovery periods.
Conclusion
Understanding and utilizing the appropriate dental chair positions is essential for providing high-quality dental care.
Each position, from upright to Fowler's, serves a specific purpose and offers distinct benefits for both the dentist and the patient.
By mastering these positions, dental professionals can ensure better ergonomics, improved procedure efficiency, and enhanced patient comfort.
Whether it’s routine check-ups or complex surgical procedures, the right chair position can make a significant difference in the overall dental experience.
Proper use of dental chair positions can lead to improved outcomes, greater patient satisfaction, and a more comfortable and efficient working environment for dental practitioners.